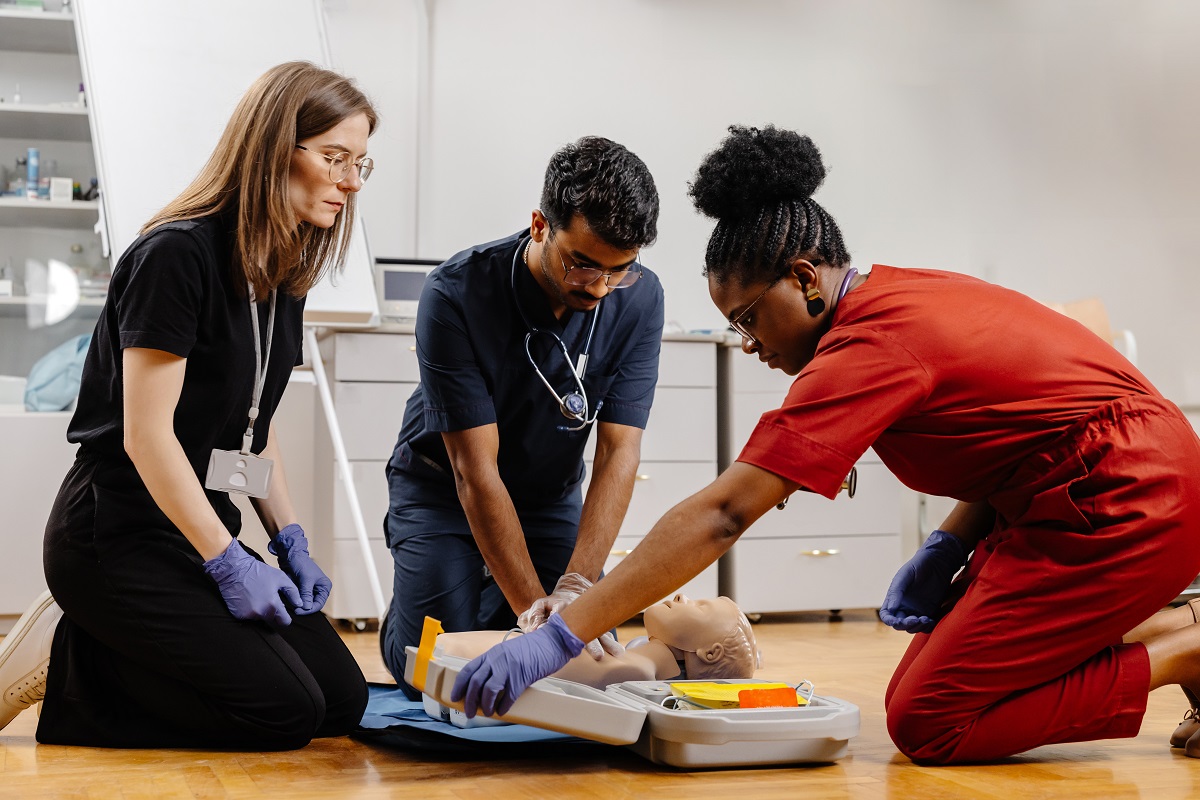
Basic Life Support (BLS) is a core requirement in modern nursing. Hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities expect nurses to be trained in recognizing cardiac arrest, performing high-quality CPR, and using an AED. Having BLS for nurses in Maryland is not just about meeting job requirements—it’s about being ready to save lives in critical situations.
BLS training equips healthcare professionals to respond quickly and effectively during life-threatening emergencies. For nurses, this skill set is essential to ensuring patient safety, meeting employment standards, and maintaining professional credibility.
This guide breaks down what BLS for nurses really means, why it matters, and how to find the right program to keep your skills current.
Key Takeaways
- BLS for nurses is a mandatory training covering CPR, AED use, and airway management.
- Most healthcare employers require nurses to maintain valid BLS certification.
- Choosing an AHA-approved BLS course ensures compliance with hospital and state standards.
- BLS certification typically lasts two years and must be renewed regularly.
What is BLS in Nursing?
The primary use of Basic Life Support (BLS) is to provide immediate care during life-threatening emergencies such as cardiac arrest, choking, or respiratory failure. It helps sustain life until advanced medical treatment becomes available.
In healthcare, BLS is a set of emergency procedures—high-quality CPR, AED use, and airway management—designed for medical professionals. Unlike community CPR, BLS for nurses emphasizes quick assessment, clinical decision-making, and team-based response in critical care situations.
How does BLS apply to nurses in different settings?
- Hospitals: Nurses respond to code blue situations and stabilize patients before advanced interventions.
- Clinics: Nurses use BLS to act quickly if a patient collapses in outpatient care.
- Long-term care facilities: BLS ensures residents in emergencies receive immediate support while waiting for EMS.
BLS for nurses fills the vital gap between the start of a medical emergency and the arrival of advanced care, making it one of the most essential skills in nursing.
Why Nurses Should Consider BLS Training
- Professional requirement
Most healthcare employers require nurses to maintain valid BLS certification as part of their employment. Hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities often require nurses to obtain specific credentials before they can work directly with patients. - Improved patient safety
BLS training gives nurses the confidence to act quickly in emergencies. Being able to perform high-quality CPR, use an AED, and manage airways can make the difference between life and death. A study from the National Library of Medicine shows that rapid BLS response significantly increases survival rates in cardiac arrest cases. - Career advantage
Nurses with up-to-date BLS training demonstrate preparedness and professionalism. Employers view this as an essential qualification, and it may give applicants a competitive edge when seeking jobs in high-demand healthcare settings. - Peace of mind
Beyond compliance, BLS for nurses ensures that professionals feel ready and equipped to handle emergencies—protecting both patients and their own professional credibility.
Finding a Suitable BLS Program
Selecting the right BLS certification program is an important step for every nurse. Since most employers in Maryland require American Heart Association training, it’s best to choose a provider that is AHA-approved to ensure your card will be accepted in hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
Training formats available for nurses include:
- In-person courses – Best for first-time learners or those who want extensive practice with manikins and real-time instructor feedback.
- Blended learning – A combination of online coursework followed by a short, hands-on skills session with an instructor. This option is convenient for busy nurses who need flexibility without losing the required practice.
- Online renewal courses – In some cases, nurses can complete the theory portion fully online, but most employers still require a hands-on component to validate CPR and AED skills.
What to consider when choosing a program:
- Employer requirements – Always confirm if your hospital or healthcare organization has specific rules on training providers.
- Cost and location – Some programs may be more affordable, but accessibility and scheduling matter too, especially for shift-working nurses.
- Renewal policies – AHA BLS certification is valid for two years, after which renewal is required. Choosing a provider that offers renewal options and reminders helps nurses stay compliant without interruptions.
- Credibility – Beware of uncertified providers. Only AHA-recognized courses guarantee compliance across healthcare facilities.
In addition to training centers, some healthcare organizations partner with home care agencies and professional development providers. For example, Comfi-kare CPR offers nurses everything they need to complete their BLS certification and keep it current, making it a reliable option for both first-time training and renewals.
Ultimately, investing in a reputable BLS certification program not only fulfills job requirements but also ensures you are fully prepared to act quickly and effectively in emergencies.
Keeping Your BLS Skills Current
Earning a BLS certification is only the first step. For nurses, staying current is just as important as getting certified. The American Heart Association requires renewal every two years, ensuring that healthcare professionals keep their knowledge and skills sharp.
Why renewal matters:
- Skill retention – CPR and AED techniques can fade without practice, and refreshers reinforce proper response.
- Updated guidelines – The AHA regularly updates BLS protocols based on new research. Renewal courses ensure nurses are trained in the latest evidence-based practices.
- Employer compliance – Hospitals and clinics often monitor certification expiration closely. An expired card can affect a nurse’s ability to work directly with patients.
How to stay on track:
- Enroll in renewal courses before your card expires—many providers send reminder notices.
- Take advantage of skills practice sessions or mock code drills offered by your workplace.
- Keep a digital copy of your BLS eCard for easy access and verification.
By keeping BLS for nurses up to date, you ensure readiness in emergencies, maintain professional credibility, and continue meeting employer standards.
Conclusion
BLS for nurses is more than a requirement—it’s a vital skill that protects patients and strengthens professional practice. Staying certified ensures you are always ready to respond in emergencies, whether in a hospital, clinic, or long-term care setting.
For reliable training and renewals in Maryland, turn to Comfi-kare CPR—your trusted partner in keeping BLS certification current and accessible. We provide courses in BLS, CPR, AED, and many other emergency training programs designed to meet the needs of healthcare professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions About BLS For Nurses
What is BLS in nursing?
In nursing, Basic Life Support (BLS) refers to emergency care skills like CPR, AED use, and airway management. It is required for nurses to ensure they can respond quickly and effectively in life-threatening situations.
What is a BLS certification in healthcare?
A BLS certification is official proof that a healthcare professional has completed training in life-saving procedures. For nurses, it shows they are prepared to handle emergencies such as cardiac arrest, choking, or respiratory failure.
How do I get my BLS certificate?
To earn a BLS certificate, you must complete an approved training course, usually through the American Heart Association (AHA) or a recognized provider. This includes online learning, a skills test, and hands-on practice with an instructor.
How long does BLS take to learn?
Most BLS courses take about 3 to 4 hours to complete. The exact time depends on whether you choose in-person, blended, or renewal training.
How long is BLS valid for?
A BLS certification is valid for two years. After that, nurses must complete a renewal course to keep their certification current and maintain compliance with employer and healthcare standards.